HTTP Verb Tampering
Table of Contents
- Introduction to HTTP Verb Tampering
- Insecure Configurations
- Insecure Coding in Input Sanitasation
- Example of bypassing authentication by changing request method
- Examine which HTTP methods the website takes
- Bypassing Security Filters by changing method to acheive command injection
Introduction to HTTP Verb Tampering
- exploits web servers that accept many HTTP verbs and method, did not configure to limit to GET/POST
- send malicious requests using unexpected methods
| Verb | Description |
|---|---|
HEAD | Identical to a GET request, but its response only contains the headers, without the response body |
PUT | Writes the request payload to the specified location |
DELETE | Deletes the resource at the specified location |
OPTIONS | Shows different options accepted by a web server, like accepted HTTP verbs |
PATCH | Apply partial modifications to the resource at the specified location |
Insecure Configurations
Apache vulnerable example in .htaccess file
<Directory "/var/www/html/admin">
AuthType Basic
AuthName "Admin Panel"
AuthUserFile /etc/apache2/.htpasswd
<Limit GET>
Require valid-user
</Limit>
</Directory>
Tomcat vulnerable example web.xml
<security-constraint>
<web-resource-collection>
<url-pattern>/admin/*</url-pattern>
<http-method>GET</http-method>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<role-name>admin</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
ASP.NET vulnerable example in web.config
<system.web>
<authorization>
<allow verbs="GET" roles="admin">
<deny verbs="GET" users="*">
</deny>
</allow>
</authorization>
</system.web>
the configuration specifies authentication in order to use GET and POST requests, attacker can still use a different HTTP method (like HEAD) to bypass this authentication mechanism altogether -> authentication bypass and allows attackers to access web pages and domains they should not have access to
Insecure Coding in Input Sanitasation
$pattern = "/^[A-Za-z\s]+$/";
if(preg_match($pattern, $_GET["code"])) {
$query = "Select * from ports where port_code like '%" . $_REQUEST["code"] . "%'";
...SNIP...
}
REQUEST accepts both GET and POST, but sanitisation only covers GET. in PHP, look for $_POST, $_GET
developer mitigated SQL-injection using this. We can see that the sanitization filter is only being tested on the GET parameter. In this case, use POST request to SQL inject. The request would pass the security filter, which would make the function vulnerable to SQLi.
Example of bypassing authentication by changing request method
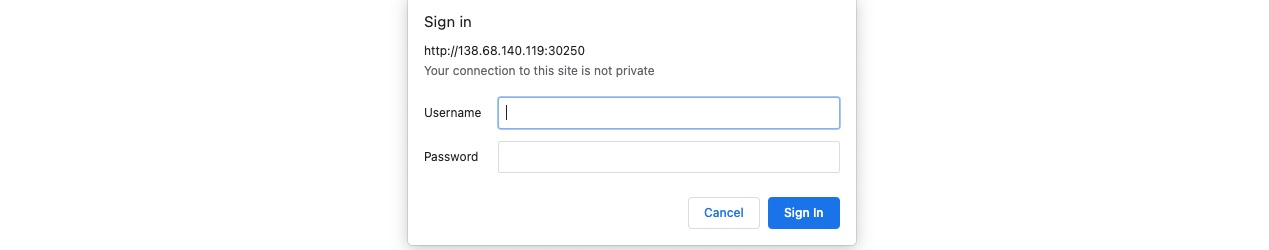
We get a HTTP Basic Auth prompt
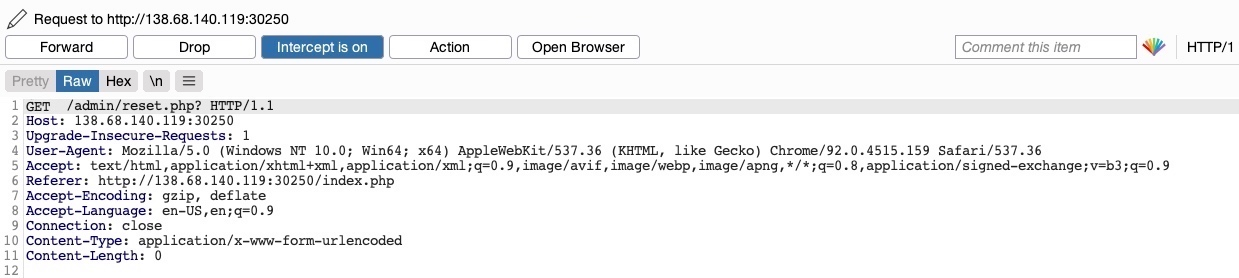
Intercept using Burp
The page uses a GET request, we can send a POST request and see whether the web page allows POST requests (i.e., whether the Authentication covers POST requests). To do so, we can right-click on the intercepted request in Burp and select Change Request Method, and it will automatically change the request into a POST request:
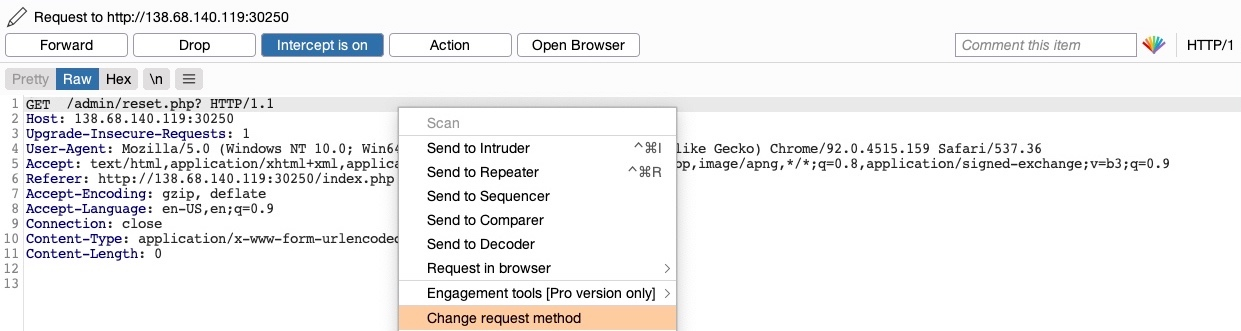
Unfortunately in this case it does not work.
Examine which HTTP methods the website takes
> curl -i -X OPTIONS http://SERVER_IP:PORT/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date:
Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
Allow: POST,OPTIONS,HEAD,GET
Content-Length: 0
Content-Type: httpd/unix-directory
Based on this, alter the header in burp suite to bypass authentication is authentication only targets get or post request
Bypassing Security Filters by changing method to acheive command injection
If we try to enter "test;" it does not allow. The code checks for patterns and deny requests. However if I change the method, it does not check.