Port Forwarding
What is Port Forwarding?
- redirect communication request from one port to another
- Use application layer protocols (SSH, SOCKS) to encapsulate forwarded traffic, which can bypass firewalls
> nmap -sT -p22,3306 10.129.202.64
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
3306/tcp closed mysql
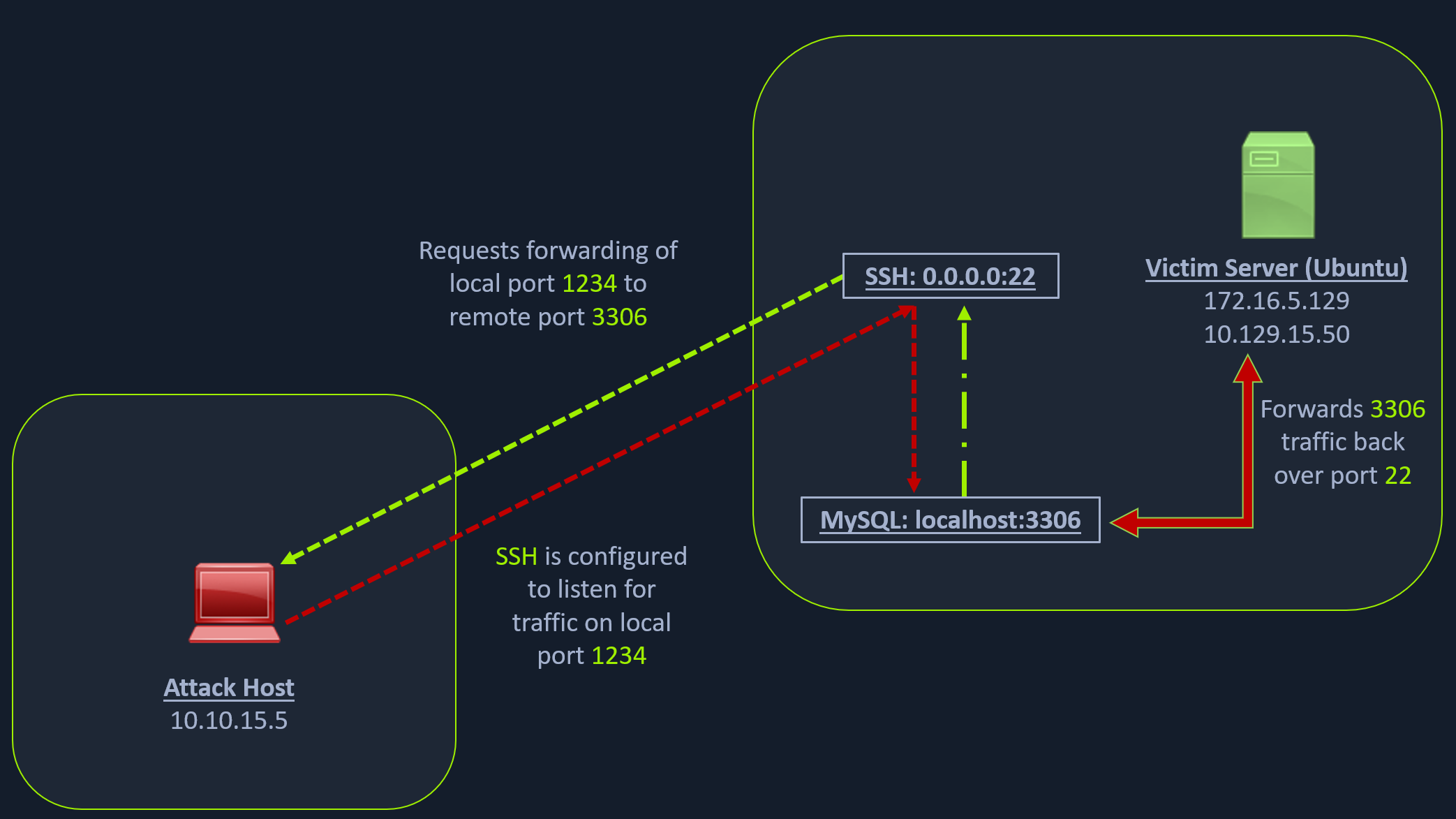
In the above diagram,
- Port 22(SSH) is open, but port 3306(MySQL) is closed from external communication
- We can SSH into the server and interact with MySQL internally
- Alternatively, we can forward MySQL to our localhost on port 1234 to access it locally
- Accessing it locally allows us to execute a remote exploit
Local Port Forwarding
on our attacking machine:
ssh -L 1234:localhost:3306 ubuntu@10.129.202.64
this authenticates into target machine's SSH server, and requests the machine to forward traffic from 3306 to 1234, which we connect to
The -L command tells the SSH client to request the SSH server to forward all the data we send via the port 1234 to localhost:3306 on the Ubuntu server
forwarding multiple ports
ssh -L 1234:localhost:3306 -L 8080:localhost:80 ubuntu@10.129.202.64
Verify Port Forwarded
netstat
> netstat -antp | grep 1234
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
will not be shown, you would have to be root to see it all.)
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:1234 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 4034/ssh
tcp6 0 0 ::1:1234 :::* LISTEN 4034/ssh
nmap
> nmap -sV -p1234 localhost
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-02-24 12:18 EST
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
1234/tcp open mysql MySQL 8.0.28-0ubuntu0.20.04.3
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.18 seconds